Plato
Plato (Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy)
Plato (429?-347 B.C.E.) is, by any reckoning, one of the most dazzling writers in the Western literary tradition and one of the most penetrating, wide-ranging, and influential authors in the history of philosophy.
|
|
|
Plato
Plato is one of the world's best known and most widely read and studied philosophers. He was the student of Socrates and the teacher of Aristotle, and he wrote in the middle of the fourth century B.C.E. in ancient Greece. Though influenced primarily by Socrates, to the extent that Socrates is usually the main character in many of Plato's writings, he was also influenced by Heraclitus, Parmenides, and the Pythagoreans.
There are varying degrees of controversy over which of Plato's works are authentic, and in what order they were written, due to their antiquity and the manner of their preservation through time. Nonetheless, his earliest works are generally regarded as the most reliable of the ancient sources on Socrates, and the character Socrates that we know through these writings is considered to be one of the greatest of the ancient philosophers.
Plato's middle to later works, including his most famous work, the Republic, are generally regarded as providing Plato's own philosophy, where the main character in effect speaks for Plato himself. These works blend ethics, political philosophy, moral psychology, epistemology, and metaphysics into an interconnected and systematic philosophy. It is most of all from Plato that we get the theory of Forms, according to which the world we know through the senses is only an imitation of the pure, eternal, and unchanging world of the Forms. Plato's works also contain the origins of the familiar complaint that the arts work by inflaming the passions, and are mere illusions. We also are introduced to the ideal of "Platonic love:" Plato saw love as motivated by a longing for the highest Form of beauty—The Beautiful Itself, and love as the motivational power through which the highest of achievements are possible. Because they tended to distract us into accepting less than our highest potentials, however, Plato mistrusted and generally advised against physical expressions of love.
There are varying degrees of controversy over which of Plato's works are authentic, and in what order they were written, due to their antiquity and the manner of their preservation through time. Nonetheless, his earliest works are generally regarded as the most reliable of the ancient sources on Socrates, and the character Socrates that we know through these writings is considered to be one of the greatest of the ancient philosophers.
Plato's middle to later works, including his most famous work, the Republic, are generally regarded as providing Plato's own philosophy, where the main character in effect speaks for Plato himself. These works blend ethics, political philosophy, moral psychology, epistemology, and metaphysics into an interconnected and systematic philosophy. It is most of all from Plato that we get the theory of Forms, according to which the world we know through the senses is only an imitation of the pure, eternal, and unchanging world of the Forms. Plato's works also contain the origins of the familiar complaint that the arts work by inflaming the passions, and are mere illusions. We also are introduced to the ideal of "Platonic love:" Plato saw love as motivated by a longing for the highest Form of beauty—The Beautiful Itself, and love as the motivational power through which the highest of achievements are possible. Because they tended to distract us into accepting less than our highest potentials, however, Plato mistrusted and generally advised against physical expressions of love.
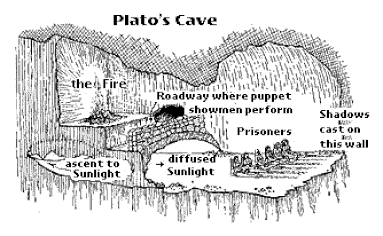
Allegory of the Cave
The Allegory of the Cave explains Plato's explanation of people who are untutored to the World of the Forms. The Allegory shows the prisoners chained in a cave who are unable to turn their heads. All they can see is the wall of the cave. Behind them a fire burns. Between the fire and the prisoners there is a ledge where puppeteers who are behind the prisoners and hold puppets that cast shadows on the walls of the cave. The prisoners are unable to see the puppets or the real objects which pass behind them. What the prisoners do see and hear are shadows and echoes cast by the objsects they are unable to see.
The Prisoners would mistake the appearances for reality and would think that the things they see on the wall (the shadows) were real; they would not know the real causes of the shadows. The Prisoners when they talk are talking about shadows where as they think they are reality. Plato meant that the prisoners would be mistaken, for example if a prisoner says “That’s a book” he thinks that the word “book” refers to the very thing he is looking at. But he would be wrong. He’s only looking at a shadow. The real referent of the word “book” he cannot see. To see it, he would have to turn his head around. Plato suggested that the language we use are not names of the physical objects we can see but they are actually the names of things we cannot see. When the prisoners are released they can turn their heads and see the real objects they can then realise their errors. The prisoners would then understand the Forms.
The World of the Forms
Plato: A Theory of Forms
Your complimentary articles Plato For the non-philosopher, Plato's Theory of Forms can seem difficult to grasp. If we can place this theory into its historical and cultural context perhaps it will begin to make a little more sense. Plato was born somewhere in 428-427 B.C., possibly in Athens, at a time when Athenian democracy was already well developed.
|
|
|